
| Friends of Five Creeks |
Water Quality Monitoring: pH
pH
- A range of pH 6.5 to pH 8.2 is optimal for most organisms.
- Most organisms have adapted to life in water of a specific pH and may die if it changes even slightly. The toxicity level of ammonia to fish, for example, varies tremendously within a small range of pH values.
- Acid rain containing nitric and sulferic acids can sharply lower the pH of a stream as the rain runs quickly off streets and roofs into creeks. Acidic water can cause heavy metals such as copper and aluminum to be released into the water. Copper from worn automobile brake pads is often present in runoff.
- Rapidly growing algae remove carbon dioxide from the water during photosynthesis, which can result in a significant increase in pH levels.
Test Equipment
- LaMotte pH Tester 2 (Code 5-1769)
- Yellow-Seven Buffer Solution for calibration
- Small plastic cup
- Wash bottle containing demineralized water
- Waste container
Procedure
Calibration
- It may be more convenient to perform the calibration indoors just before heading to the test site.
- Remove the cap on the tester (5-1769) and fill the small plastic cup with the buffer solution far enough that the electrode on the bottom of the tester will be covered, but the tester won't fall in to over the maximum immersion level marking and the buffer solution won't overflow the cup.
- Press the on/off button once to turn on the tester and leave it in the buffer solution for one or two minutes to adjust to the buffer solution temperature.
- Press the "cal" button to enter calibration mode and stir gently while waiting for the displayed value to stabilize.
- When the reading stabilizes, press the "hold/con" button to confirm and complete the calibration. Press the on/off button again to turn the tester off.
- Rinse the electrode off with demineralized water and pour the used water and used buffer solution into the waste container.
- Replace the cap.
Measurement
- At the test site remove the cap, press the on/off button to turn on the tester, and dip the electrode two to three centimeters into the creek at arm's length. It may be possible to hold a thermometer or conductivity tester at the same time and make all measurements at once.
- Wait three minutes for the tester to adjust to the water temperature and stabilize. Stir slowly back and forth while waiting.
- Note the reading or press the "hold/con" button to save it until it can be written down and record it.
- Press the on/off button again to turn it off and replace the cap on the tester.
Water Quality Index
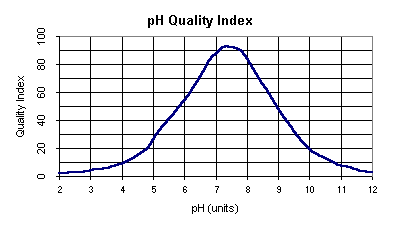
Note: If pH is less than 2.0 or greater than 12.0,
the quality index equals 0.
Calculations
- Convert pH to water quality index.